Operational Shift
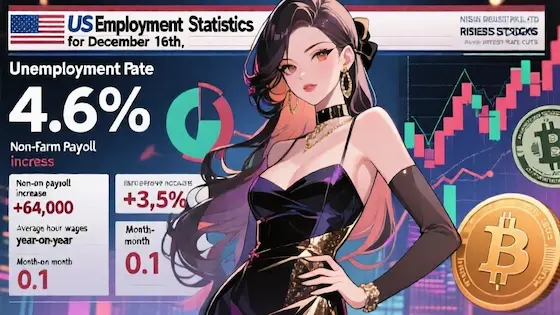
The European Central Bank (ECB) announced significant changes to its open market operations, shifting from regular to structural operations. This move aims to permanently reduce liquidity in the eurozone banking system.
Liquidity Management
The change involves reducing the frequency of targeted longer-term refinancing operations (TLTROs), the primary tool for injecting liquidity. The ECB will now rely more on minimum reserve requirements and fine-tuning operations to manage short-term liquidity needs.
Rationale Behind the Change
The ECB cited several reasons for the shift. Excess liquidity, accumulated through past stimulus programs, is now seen as a potential inflation risk. The new approach also aims to strengthen the transmission of monetary policy and encourage banks to rely more on market-based funding.
New Tools and Frameworks
The ECB is also developing a new liquidity management framework. This includes a standing borrowing facility, offering banks a backstop source of liquidity at a penalty rate. The central bank will also introduce a tiered remuneration system for reserve holdings, incentivizing banks to hold reserves closer to the minimum requirement.
Market Impact
The changes are expected to gradually reduce excess liquidity, potentially leading to higher interbank lending rates. This could impact banks’ profitability and borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. The ECB emphasized a smooth transition to minimize market disruption.
Long-Term Implications
The move represents a significant shift in the ECB’s operational strategy. By reducing its footprint in liquidity provision, the ECB aims to create a more market-driven financial system. The long-term effects of this change will depend on various factors, including economic growth and inflation dynamics.